
What is collagen?
Collagen is the primary structural protein in connective tissues, including skin, tendons, cartilage, muscles, ligaments, bones, and teeth (1,2,3).
It makes up around 25-30% of all the protein in your body and plays a crucial role in organ development, wound healing, tissue repair, and even bone health and blood vessel repair (4).
As collagen affects the structural, mechanical, and tissue-building properties of your body, it's an incredibly important protein in the aging process (5).
Unfortunately, collagen production starts to decline from around 18-29 years of age, and after 40 years, your body may lose up to 1% of collagen every year. By the time you reach 80 years old, collagen production can decrease by 75% compared to that of a young adult (6,7).
That's why it's essential to support collagen production as early as possible. Taking steps to maintain healthy collagen levels can help keep your body functioning optimally throughout your life.
Figure 1. Sources and applications of collagen
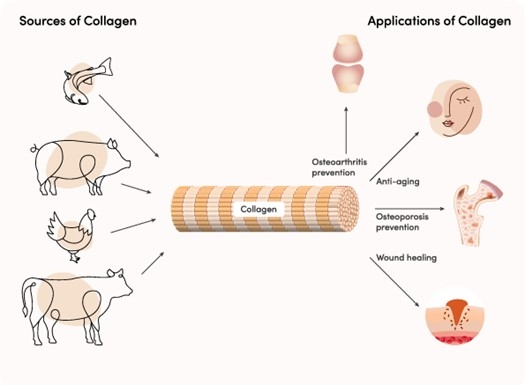
What are the different types of collagen?
There are 29 different kinds of collagen. The most common types in collagen supplements are types I, II, and III. These types make up 80-90% of the collagen in our bodies (8,9). Types I and III are mainly found in the skin, while types II and IV mostly form the structural matrix in cartilage (8).
How can collagen help my skin?
Collagen gives skin its strength and elasticity by forming the extracellular matrix along with hyaluronic acid, reticulin, and elastin. This matrix serves as a support network for specialised skin cells such as fibroblasts.
This network becomes increasingly fragmented as we age (7). As we age, our body also generates enzymes that can break down collagen fibres. This results in decreased production of new collagen, which can exacerbate the problem (10).
Skin aging has become a common worry, even among younger people, due to the extended lifespan (2). The process of skin aging is influenced by both internal factors such as genetics, and external factors including sun exposure, air pollution, tobacco smoke, and poor diet (5).
Skin aging is a natural, unavoidable process. However, taking bioactive collagen peptides can help delay the process. Collagen peptides accumulate in the skin, improving its condition by reducing oxidative stress, preventing inflammation, regulating cell behaviour, and maintaining extracellular matrix homeostasis (11,12).
The peptides are sourced from naturally occurring collagen that undergoes enzymatic hydrolysis processing. Following digestion, they travel through the bloodstream to the skin, or other parts of the body, where they facilitate the formation of fresh collagen fibres (13,14).
Supplementing with hydrolysed collagen may enhance skin density, elasticity, and hydration while reducing facial wrinkles. Typically, visible outcomes are noticeable within 90 days of consumption and remain sustained for up to 4 weeks after discontinuing the supplement (2,15).
The body uses collagen protein wherever it’s needed, meaning that it may not specifically be utilized by the skin (16). Other ways to improve skin collagen include avoiding smoking, using sunscreen and eating a healthy, balanced diet (17).
How can collagen help my bones and joints?
As we age, the collagen content in our bones and joints decreases. This natural process is further worsened by being overweight or leading a sedentary lifestyle, as well as experiencing inflammation and joint or bone damage (for example, from strenuous physical activities). Hormonal changes may also contribute (5).
Hydrolysed collagen , such as improving bone strength, density, and mineral mass, enhancing joint mobility, reducing stiffness and pain, and boosting joint stability and recovery (5,18).
Collagen sources
Collagen is a protein that exists naturally in animal flesh such as meat and fish, which are rich in connective tissue. Nevertheless, there are also several plant and animal sources that provide the necessary materials for collagen production in our bodies.
The majority of collagen for oral supplements in the marketplace is obtained from animal-origin raw material. Collagen is extracted from industrial by-products, such as bones, cartilage, tendons, and the skin of cattle, pigs, chickens, fish, or other marine organisms (19,20,21).
The collagen may undergo a hydrolysis process to obtain bioactive peptides. Peptides from hydrolysed collagens have a high bioavailability allowing them to reach the bloodstream (18).
Collagen obtained from marine sources such as fish scales and fish skin is abundant in type I collagen (21). It is more easily absorbed, and may have a lower likelihood of causing inflammation or containing contaminants compared to animal-derived sources (22).
Certain foods are great for promoting collagen production. Foods that are high in protein and contain glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline amino acids are particularly helpful. These include fish, poultry, meat, eggs, dairy, legumes, and soy.
Incorporating plant-based foods like mangos, kale extract, tomato paste, and pomegranate juice can boost collagen production and prevent skin collagen breakdown.
You can also get a boost of vitamin C from many fruits and vegetables, which is a necessary component for collagen synthesis (23,24,25).
“Vegan collagen” typically does not contain collagen, but is made up of a blend of ingredients including plant extracts, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals (18).
Safety
Collagen supplements are generally considered safe, and there have been no reported adverse events. However, allergic reactions may occur. People with shellfish allergies may experience a reaction, including anaphylaxis if they consume hydrolysed fish collagen (26).
Always use supplements with caution and according to instructions from a practitioner or the product label.
Key takeaway
As we get older, our body's production of collagen decreases. Collagen is a vital protein that gives structure to connective tissue. To combat this, it can be helpful to add collagen to our diet or take supplements. Collagen can aid in slowing down or reducing the impact of aging on our skin, and it also supports bone and joint health.
It’s important to speak with a healthcare provider before taking any supplements, as they may interact with medications or have other side effects.


