Monographs licensed from Therapeutic Research Center, LLC
Beta-methylphenethylamine (bmpea)
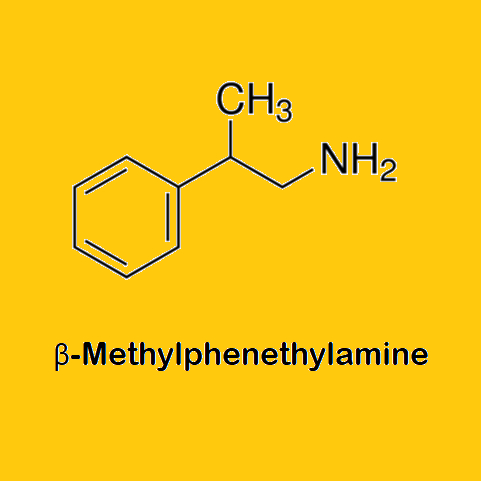
Scientific names: 2-Phenylpropan-1-amine
Alternate names: 1-Amino-2-Phenylpropane, 1-Phenyl-1-Methyl-2-Aminoethane, 2-Aminoisopropylbenzene, 2-Phenyl-1-Propanamin, 2-Phenyl-1-Propanamine, 2-Phenylpropylamine, Alpha-Benzylethylamine, ß-Me-PEA, ß-Methylphenethylamine, Beta-Me-PEA, Beta-Methylbenzeneethanamine, Beta-Methylphenylethylamine, Beta-Methylphenylethylamine HCl, Beta-Methylphenyl-Ethylamine, BMPEA, Beta-Phenylpropylamine, R-Beta-Methylphenethylamine, R-Beta-Methylphenethylamine HCl
Actions: Cardiovascular, Neurological
Scientific names: 2-Phenylpropan-1-amine
Alternate names: 1-Amino-2-Phenylpropane, 1-Phenyl-1-Methyl-2-Aminoethane, 2-Aminoisopropylbenzene, 2-Phenyl-1-Propanamin, 2-Phenyl-1-Propanamine, 2-Phenylpropylamine, Alpha-Benzylethylamine, ß-Me-PEA, ß-Methylphenethylamine, Beta-Me-PEA, Beta-Methylbenzeneethanamine, Beta-Methylphenylethylamine, Beta-Methylphenylethylamine HCl, Beta-Methylphenyl-Ethylamine, BMPEA, Beta-Phenylpropylamine, R-Beta-Methylphenethylamine, R-Beta-Methylphenethylamine HCl
Actions: Cardiovascular, Neurological
Beta-methylphenethylamine (BMPEA) is a stimulant chemical that is made in the lab. It's similar to amphetamine and may be illegally included in some supplements.
BMPEA might increase blood pressure, heart rate, and also stimulate the brain. Because of this, it's often added to products for weight loss and athletic performance.
People use BMPEA for obesity, athletic performance, memory, and other purposes, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
According to the US FDA, BMPEA does not meet the definition of a dietary supplement. But it is still found in some supplement products. Many of these supplements list Acacia rigidula on the product label. But many of these products do not contain Acacia rigidula, and if they do, BMPEA that was made in a lab has been added as well. BMPEA is also banned by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) for use during competitive sports.
When taken by mouth: BMPEA is possibly unsafe. It has stimulant effects that might cause serious heart-related side effects, such as stroke and heart attack.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: BMPEA is possibly unsafe to take by mouth. It has stimulant effects that might cause serious side effects, such as stroke and heart attack.
High blood pressure: BMPEA has stimulant effects. It can increase blood pressure. Taking BMPEA might make high blood pressure worse.
Surgery: BMPEA has stimulant effects. It can increase blood pressure and heart rate. Taking BMPEA might interfere with surgery by increasing blood pressure and heart rate. Stop taking BMPEA at least 2 weeks before surgery.
There is interest in using BMPEA for a number of purposes, but there isn't enough reliable information to say whether it might be helpful.
BMPEA has stimulant effects similar to amphetamine. Dietary supplements that contain BMPEA usually list Acacia rigidula on the product label. But many of these products do not contain Acacia rigidula, and if they do, BMPEA that was made in a lab has been added as well. Avoid products with BMPEA or Acacia rigidula on the label.
Dietary supplements that contain BMPEA are considered misbranded by the US FDA. BMPEA is also banned by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) for use during competitive sports.
Interactions with pharmaceuticals
Medications changed by the liver (Cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) substrates)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Some medications are changed and broken down by the liver. BMPEA might change how quickly the liver breaks down these medications. This could change the effects and side effects of these medications.
Medications changed by the liver (Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) substrates)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Some medications are changed and broken down by the liver. BMPEA might change how quickly the liver breaks down these medications. This could change the effects and side effects of these medications.
Stimulant Drugs
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Stimulants, such as amphetamines and cocaine, speed up the nervous system. By speeding up the nervous system, stimulant medications can increase blood pressure and speed up the heartbeat. BMPEA also has stimulant effects. Taking BMPEA along with stimulant drugs might cause serious problems including increased heart rate and high blood pressure.
Interactions with herbs & supplements
Herbs and supplements with stimulant properties: BMPEA might have stimulant effects. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might increase the chance of side effects, including rapid heartbeat and high blood pressure. Examples of supplements with this effect include 1,3-DMAA, bitter orange, caffeine-containing products, DMHA, and ephedra.
There are no known interactions with foods.
vital.ly has licensed monographs from TRC Healthcare.
This monograph was last reviewed on 31/01/2024 11:00:00 and last updated on 08/12/2020 19:42:30. Monographs are reviewed and/or updated multiple times per month and at least once per year.
Natural Medicines disclaims any responsibility related to medical consequences of using any medical product. Effort is made to ensure that the information contained in this monograph is accurate at the time it was published. Consumers and medical professionals who consult this monograph are cautioned that any medical or product related decision is the sole responsibility of the consumer and/or the health care professional. A legal License Agreement sets limitations on downloading, storing, or printing content from this Database. No reproduction of this monograph or any content from this Database is permitted without written permission from the publisher. It is unlawful to download, store, or distribute content from this site.
Natural Medicines rates safety based on scientific evidence according to the following scale: Likely Safe, Possibly Safe, Possibly Unsafe, Likely Unsafe, Unsafe, and Insufficient Evidence to Rate. For more information about Natural Medicines’ Safety Rating System,
click here.
The Natural Medicines Effectiveness Ratings are assigned for specific indications. A product might be rated "Possibly Effective" for one condition, but be rated "Likely Ineffective" for another condition, depending on the evidence. For more info
click here.