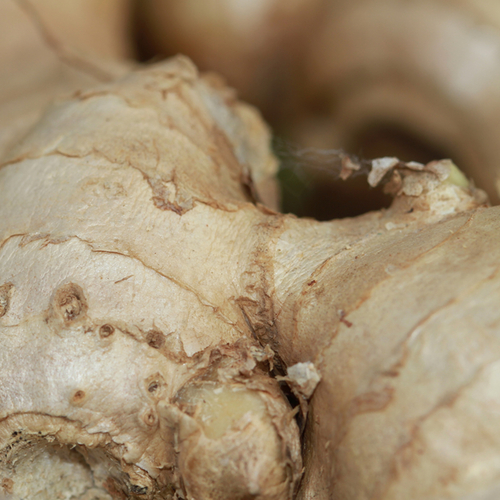
Background
Ginger contains chemicals that might reduce nausea and swelling. These chemicals seem to work in the stomach and intestines, but they might also help the brain and nervous system to control nausea.
People commonly use ginger for menstrual cramps, osteoarthritis, and morning sickness. It is also used for diabetes, motion sickness, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support most of these uses. There is also no good evidence to support using ginger for COVID-19.
Safety Safety definitions
When applied to the skin: Ginger is possibly safe when used short-term. It might cause skin irritation for some people.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy: Ginger is likely safe when eaten in foods. It is possibly safe when taken by mouth as medicine during pregnancy. It might increase the risk of bleeding, so some experts advise against using it close to the delivery date. But it appears to be safe to use for morning sickness without harm to the baby. Talk to your healthcare provider before using ginger during pregnancy.Breast-feeding: Ginger is likely safe when eaten in foods. There isn't enough reliable information to know if taking larger amounts of ginger is safe when breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
Children: Ginger is possibly safe when taken by mouth for up to 4 days by teenagers around the start of their period.
Bleeding disorders: Taking ginger might increase your risk of bleeding.
Heart conditions: High doses of ginger might worsen some heart conditions.
Surgery: Ginger might slow blood clotting. It might cause extra bleeding during and after surgery. Stop using ginger at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Effectiveness
- Menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea). Taking ginger by mouth during the first 3-4 days of a menstrual cycle somewhat reduces painful menstrual periods. It seems to work about as well as some pain medications, like ibuprofen, mefenamic acid, or Novafen. Taking ginger along with medicines such as mefenamic acid also seems to be helpful.
- Osteoarthritis. Taking ginger by mouth can slightly reduce pain in some people with osteoarthritis. But applying ginger gel or oil to the knee doesn't seem to help.
- Morning sickness. Taking ginger by mouth seems to reduce nausea and vomiting in some people during pregnancy. But it might work slower or not as well as some drugs used for nausea.
- Nausea and vomiting caused by cancer drug treatment. Taking ginger by mouth doesn't reduce nausea or vomiting caused by chemotherapy.
- Muscle soreness caused by exercise. Taking ginger by mouth doesn't reduce or prevent muscle pain from exercise.
- Motion sickness. Taking ginger by mouth up to 4 hours before travel doesn't prevent motion sickness.
Dosing & administration
Interactions with pharmaceuticals
Cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune)
Interaction Rating=Minor Be watchful with this combination.
Taking ginger two hours before taking cyclosporine might increase how much cyclosporine the body absorbs. This might increase the side effects of cyclosporine. But ginger does not seem to affect how much cyclosporine the body absorbs when they are taken at the same time.
Losartan (Cozaar)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Ginger can increase how much losartan the body absorbs. Taking ginger along with losartan might increase the effects and side effects of losartan.
Medications changed by the liver (Cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) substrates)
Interaction Rating=Minor Be watchful with this combination.
Some medications are changed and broken down by the liver. Ginger might change how quickly the liver breaks down these medications. This could change the effects and side effects of these medications.
Medications changed by the liver (Cytochrome P450 2B6 (CYP2B6) substrates)
Interaction Rating=Minor Be watchful with this combination.
Some medications are changed and broken down by the liver. Ginger might change how quickly the liver breaks down these medications. This could change the effects and side effects of these medications.
Medications changed by the liver (Cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9) substrates)
Interaction Rating=Minor Be watchful with this combination.
Some medications are changed and broken down by the liver. Ginger might change how quickly the liver breaks down these medications. This could change the effects and side effects of these medications.
Medications changed by the liver (Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) substrates)
Interaction Rating=Minor Be watchful with this combination.
Some medications are changed and broken down by the liver. Ginger might change how quickly the liver breaks down these medications. This could change the effects and side effects of these medications.
Medications for diabetes (Antidiabetes drugs)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Ginger might lower blood sugar levels. Taking ginger along with diabetes medications might cause blood sugar to drop too low. Monitor your blood sugar closely.
Medications for high blood pressure (Calcium channel blockers)
Interaction Rating=Minor Be watchful with this combination.
Ginger might lower blood pressure. Taking ginger along with medications that lower blood pressure might cause blood pressure to go too low. Monitor your blood pressure closely.
Medications moved by pumps in cells (P-Glycoprotein Substrates)
Interaction Rating=Minor Be watchful with this combination.
Some medications are moved in and out of cells by pumps. Ginger might change how these pumps work and change how much medication stays in the body. In some cases, this might change the effects and side effects of a medication.
Medications that slow blood clotting (Anticoagulant / Antiplatelet drugs)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Ginger might slow blood clotting. Taking ginger along with medications that also slow blood clotting might increase the risk of bruising and bleeding.
Metronidazole (Flagyl)
Interaction Rating=Minor Be watchful with this combination.
Ginger can increase how much metronidazole the body absorbs. Taking ginger along with metronidazole might increase the effects and side effects of metronidazole.
Nifedipine (Procardia)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Taking ginger along with nifedipine might slow blood clotting and increase the chances of bruising and bleeding.
Phenprocoumon (Marcoumar, others)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Phenprocoumon is used to slow blood clotting. Ginger can also slow blood clotting. Taking ginger along with phenprocoumon might increase the chances of bruising and bleeding. Be sure to have your blood checked regularly. The dose of your phenprocoumon might need to be changed.
Warfarin (Coumadin)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Warfarin is used to slow blood clotting. Ginger can also slow blood clotting. Taking ginger along with warfarin might increase the chances of bruising and bleeding. Be sure to have your blood checked regularly. The dose of your warfarin might need to be changed.
Interactions with herbs & supplements
Herbs and supplements that might slow blood clotting: Ginger might slow blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might increase the risk of bleeding in some people. Examples of supplements with this effect include garlic, ginkgo, nattokinase, and Panax ginseng.
Interactions with foods
Products
View all products- Zingiber officinale (Ginger) ext. 10 mg equiv. gingerols 1 mg
- Eleutherococcus senticosus ext. 50 mg
- Thiamine hydrochloride (Vitamin B1) 2.54 mg equiv. thiamine 2 mg
- Nicotinamide (Vitamin B3) 20 mg
- Calcium pantothenate (Vitamin B5) 9.83 mg equiv. pantothenic acid 9 mg
- Pyridoxal 5-phosphate monohydrate (P5P) 3.14 mg equiv. pyridoxine 2 mg
- Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) 60 mg
- d-alpha-Tocopheryl acetate (Vitamin E) 7.35 mg equiv. vitamin E 10 IU equiv. d-alpha-tocopherol 6.71 mg
- Biotin 80 µg
- Inositol 50 mg
- Quercetin 50 mg
- Potassium sulphate 78 mg equiv. potassium 35 mg
- Zinc glycinate monohydrate 10.64 mg equiv. zinc 3 mg
- Manganese (II) glycinate 3.695 mg equiv. manganese 1 mg
- Potassium iodide 91.8 µg equiv. iodine 70 µg
- Selenomethionine 50 µg equiv. selenium 20 µg
- Levomefolate glucosamine (Activated folate) 90 µg equiv. levomefolic acid 50 µg
- L-tyrosine 10 mg
- Lysine hydrochloride 12.5 mg equiv. lysine 10 mg
- L-serine 5 mg
- Brassica oleracea var. italica ext. 37.5 mg
- Withania somnifera ext. 25 mg
- Capsicum annuum ext. 8.33 mg
- Piper nigrum ext. 16 µg
- Levocarnitine fumarate (L-carnitine) 178.6 mg equiv. levocarnitine 100 mg
- Zingiber officinale (Ginger) ext. 135 mg
- Pisum sativum ext. 3.32 g
- Thiamine hydrochloride (Vitamin B1) 21.6 mg equiv. thiamine 17 mg
- Nicotinamide (Vitamin B3) 50 mg
- Calcium pantothenate (Vitamin B5) 54.6 mg equiv. pantothenic acid 50 mg
- Hydroxocobalamin (Vitamin B12) 200 μg
- Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) 250 mg
- L-glutamine 1.5 g
- Larix occidentalis (arabinogalactan) (Larch) 1 g
- Riboflavin 5-phosphate sodium (Activated B2) 6.58 mg equiv. riboflavin 5 mg
- Cholecalciferol 10 μg equiv. vitamin D3 400 IU
- Taurine 350 mg
- Molybdenum trioxide 77 μg equiv. molybdenum 50 μg
- Potassium iodide 66 μg equiv. iodine 50 μg
- Chromium nicotinate 193.6 μg equiv. chromium 24 μg
- Selenomethionine 125.4 μg equiv. selenium 50 μg
- Manganese gluconate 8.1 mg equiv. manganese 1 mg
- Zinc citrate dihydrate 46.6 mg equiv. zinc 15 mg
- Magnesium citrate 330 mg equiv. magnesium 50 mg
- Biotin 50 μg
- Levomefolate glucosamine (Activated folate) 360 μg equiv. levomefolic acid 200 μg
- Pyridoxal 5-phosphate (P5P) 15.7 mg equiv. pyridoxine 10 mg
- Choline bitartrate 30 mg
- L-glycine 1.5 g
- Silybum marianum ext. 150 mg
- Camellia sinensis powder 250 mg
- Oryza sativa ext. 10 g
- Calcified lithothamnion (Red algae) 156 mg equiv. calcium 50 mg
- Zingiber officinale (Ginger) ext. 135 mg
- Pisum sativum ext. 5 g
- Saccharum officinarum (Sugarcane fibre) 4 g
- Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) 250 mg
- Hydroxocobalamin (Vitamin B12) 200 μg
- Cholecalciferol 10 μg equiv. vitamin D3 400 IU
- Zinc citrate dihydrate 46.74 mg equiv. zinc 15 mg
- Oryza sativa ext. 15 g
- Glutamine 1.5 g
- Glycine 2 g
- Myo-inositol 1.25 g
- Taurine 500 mg
- Choline bitartrate 100 mg
- Thiamine hydrochloride (Vitamin B1) 21.6 mg equiv. thiamine 17 mg
- Riboflavin 5-phosphate sodium (Activated B2) 6.6 mg equiv. riboflavin 5 mg
- Nicotinamide (Vitamin B3) 50 mg
- Calcium pantothenate (Vitamin B5) 164 mg equiv. pantothenic acid 150 mg
- Pyridoxal 5-phosphate (P5P) 15.7 mg equiv. pyridoxine 10 mg
- Levomefolate glucosamine (Activated folate) 357 μg equiv. levomefolic acid 200 μg
- Biotin 50 μg
- Calcified lithothamnion (Red algae) 156 mg equiv. calcium 50 mg
- Magnesium citrate 330.46 mg equiv. magnesium 50 mg
- Manganese gluconate 8.12 mg equiv. manganese 1 mg
- Selenomethionine 123 μg equiv. selenium 50 μg
- Molybdenum trioxide 73.8 μg equiv. molybdenum 50 μg
- Potassium iodide 65.6 μg equiv. iodine 50 μg
- Chromium nicotinate 196.8 μg equiv. chromium 24 μg
- Cinnamomum cassia ext. 300 mg
- Vaccinium myrtillus ext. 250 mg
- Silybum marianum ext. 150 mg
- Acetyl levocarnitine hydrochloride (Acetyl-L-carnitine) 200 mg
- Zingiber officinale (Ginger) ext. 0.1 mL
- Iron amino acid chelate 25 mg equiv. iron 5 mg
- Withania somnifera ext. 120 mg
- Urtica dioica ext. 1 mL
- Codonopsis pilosula ext. 1 mL
- Glycyrrhiza glabra ext. 125 mg
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) 2.5 mg
- Pyridoxine hydrochloride (Vitamin B6) 2.5 mg equiv. pyridoxine 2 mg
- Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B12) 1.5 μg
- Zingiber officinale (Ginger) ext. 65 mg
- Levomefolate glucosamine (Activated folate) 445 µg equiv. levomefolic acid 250 µg
- Hydroxocobalamin (Vitamin B12) 250 µg
- Potassium iodide 98.10 µg equiv. iodine 75 µg
- Thiamine hydrochloride (Vitamin B1) 3.18 mg equiv. thiamine 2.5 mg
- Riboflavin 5-phosphate sodium (Activated B2) 3.29 mg equiv. riboflavin 2.5 mg
- Nicotinamide (Vitamin B3) 15 mg
- Calcium pantothenate (Vitamin B5) 27.29 mg equiv. pantothenic acid 25 mg
- Pyridoxal 5-phosphate monohydrate (P5P) 19.59 mg equiv. pyridoxine 12.5 mg
- Pyridoxine hydrochloride (Vitamin B6) 30.39 mg equiv. pyridoxine 25 mg
- Choline bitartrate 25 mg
- Inositol 25 mg
- Biotin 200 µg
- Magnesium ascorbate monohydrate (Vitamin C) 56.04 mg equiv. ascorbic acid 50 mg equiv. magnesium 3.47 mg
- Cholecalciferol 6.25 µg equiv. vitamin D3 250 IU
- Chromium picolinate 201.1 µg equiv. chromium 25 µg
- Magnesium citrate 308.64 mg equiv. magnesium 50 mg
- Manganese amino acid chelate 20 mg equiv. manganese 2 mg
- Molybdenum trioxide 37.5 µg equiv. molybdenum 25 µg
- Selenomethionine 62.1 µg equiv. selenium 25 µg
- Zinc citrate dihydrate 17.13 mg equiv. zinc 5.5 mg
- Silica - colloidal anhydrous 5 mg equiv. silica 2.34 mg
- Zingiber officinale (Ginger) ext. 55 mg
- Vitex agnus-castus ext. 70 mg
- Angelica polymorpha ext. 70 mg
- Paeonia lactiflora ext. 55 mg
- Glycyrrhiza uralensis ext. 55 mg
- Tetradium ruticarpum ext. 70 mg
- Ligusticum striatum ext. 55 mg
- Cinnamomum cassia ext. 55 mg
- Epimedium sagittatum ext. 55 mg
- Pyridoxine hydrochloride (Vitamin B6) 10 mg equiv. pyridoxine 8.23 mg
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) 5 mg