Lemon balm
Scientific names: Melissa officinalis
Family: Lamiaceae/Labiatae
Alternate names: Balm, Balm Mint, Bálsamo de Limón, Common Balm, Cure-All, Dropsy Plant, Honey Plant, Melisa, Melissa, Melissae Folium, Mélisse, Mélisse Citronnelle, Mélisse Officinale, Melissenblatt, Monarde, Sweet Balm, Sweet Mary, Toronjil
Actions: Antinociceptive, Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-inflammatory, Antineoplastic, Antioxidant, Antiprotozoal, Antithyroid, Antiviral, Cardiovascular, Dermatologic, Food preservation, Lipid, Immune, Neurologic/CNS, Weight loss
Background
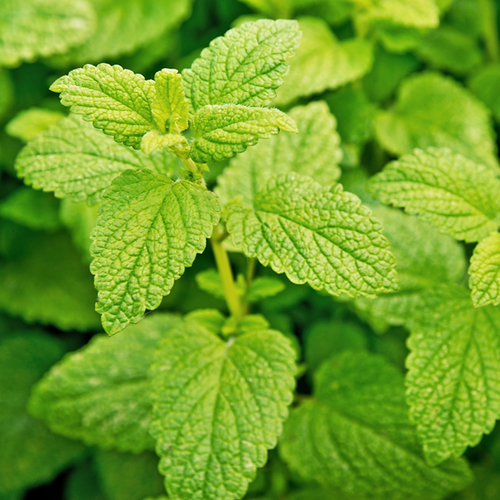
Lemon balm (Melissa officinalis) is an herb from the mint family. The leaves, which have a mild lemon aroma, are used to make medicine and flavor foods.
Lemon balm contains chemicals that seem to have a sedative and calming effect. It might also reduce the growth of some viruses and bacteria.
People use lemon balm for cold sores, anxiety, stress, insomnia, indigestion, dementia, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support many of these uses.
Lemon balm contains chemicals that seem to have a sedative and calming effect. It might also reduce the growth of some viruses and bacteria.
People use lemon balm for cold sores, anxiety, stress, insomnia, indigestion, dementia, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support many of these uses.
Safety Safety definitions
When taken by mouth: Lemon balm is likely safe when consumed in amounts found in foods. Lemon balm supplements are possibly safe when used at a dose of up to 500 mg daily for up to 6 months. Side effects are generally mild and might include increased appetite, nausea, dizziness, and wheezing. There isn't enough reliable information to know if lemon balm is safe to use for more than 6 months.
When applied to the skin: Lemon balm is possibly safe for most adults. It may cause skin irritation.
Children: Lemon balm is possibly safe when taken by mouth by children for about one month.
Surgery: Lemon balm might cause too much drowsiness if combined with medications used during and after surgery. Stop using lemon balm at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Thyroid disease: Lemon balm may change thyroid function, reduce thyroid hormone levels, and interfere with thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Avoid lemon balm if you have thyroid disease.
When applied to the skin: Lemon balm is possibly safe for most adults. It may cause skin irritation.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: There isn't enough reliable information to know if lemon balm is safe to use when pregnant or breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.Children: Lemon balm is possibly safe when taken by mouth by children for about one month.
Surgery: Lemon balm might cause too much drowsiness if combined with medications used during and after surgery. Stop using lemon balm at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Thyroid disease: Lemon balm may change thyroid function, reduce thyroid hormone levels, and interfere with thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Avoid lemon balm if you have thyroid disease.
Effectiveness
NatMed Pro rates effectiveness based on scientific evidence according to the following scale: Effective, Likely Effective, Possibly Effective, Possibly Ineffective, Likely Ineffective, Ineffective, and Insufficient Evidence to Rate.
Possibly effective Effectiveness definitions
- Depression. Taking lemon balm by mouth might help to improve symptoms of depression in adults with depression and/or anxiety.
- Cold sores (herpes labialis). Applying a lotion containing a lemon balm extract (LomaHerpan by Infectopharm) to cold sores right after they appear seems to shorten healing time and reduce symptoms.
- Stress. Taking lemon balm by mouth increases calmness, memory, and alertness in adults under mental stress. Taking lemon balm along with other ingredients might also reduce stress.
Dosing & administration
Lemon balm is available in many forms, including supplements, combination products, lotions, ointments, massage oils, and others. There isn't enough reliable information to know what an appropriate dose of lemon balm might be. Keep in mind that natural products are not always necessarily safe and dosages can be important. Be sure to follow relevant directions on product labels and consult a healthcare professional before using.
Interactions with pharmaceuticals
Sedative medications (CNS depressants)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Lemon balm might cause sleepiness and slowed breathing. Some medications, called sedatives, can also cause sleepiness and slowed breathing. Taking lemon balm with sedative medications might cause breathing problems and/or too much sleepiness.
Thyroid hormone
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Taking lemon balm seems to decrease how well thyroid hormone works in the body. Taking lemon balm with thyroid hormone might decrease the effects of the thyroid hormone.
Interactions with herbs & supplements
Herbs and supplements with sedative properties: Lemon balm might cause sleepiness and slowed breathing. Taking it along with other supplements with similar effects might cause too much sleepiness and/or slowed breathing in some people. Examples of supplements with this effect include hops, kava, L-tryptophan, melatonin, and valerian.
Herbs with thyroid activity: Lemon balm might affect the body's production of thyroid hormone. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might alter thyroid function too much and cause side effects. Examples of supplements with this effect include bugleweed and tiratricol.
Herbs with thyroid activity: Lemon balm might affect the body's production of thyroid hormone. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might alter thyroid function too much and cause side effects. Examples of supplements with this effect include bugleweed and tiratricol.
Interactions with foods
Taking lemon balm with alcohol might increase sleepiness. But it's not clear if this is a big concern.
Products
View all products$49.95
Create account
Practitioner product
RRP: $54.99$43.99Save: 20%
Create account
Per 5 g:
RRP: $63.95$57.56Save: 10%
Create account
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Per 5 g serve (Forest Berry):
- Melissa officinalis (Lemon balm) ext. 150 mg
- Crocus sativus ext. 15 mg
- L-Ornithine 250 mg
- Bacopa monnieri ext. 250 mg
- Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) 60 mg
- Calcium pantothenate (Vitamin B5) 5.45 mg equiv. pantothenic acid 5 mg
- Magnesium citrate 776 mg equiv. magnesium 112.5 mg
- Potassium citrate 104.5 mg equiv. potassium 40 mg
- L-cysteine 30 mg
- L-glycine 1.48 g
- Inositol 62.5 mg
- Phosphatidylserine enriched soy (powder) (Lecithin) 75 mg equiv. phosphatidylserine 37.5 mg
- Taurine 250 mg
$69.00
Create account
Per tablet:
RRP: $25.71$20.57Save: 20%
Create account
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Per tablet:
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
RRP: $20.99$16.79Save: 20%
Create account
vital.ly has licensed monographs from TRC Healthcare.
This monograph was last reviewed on 04/07/2024 10:00:00 and last updated on 01/06/2018 21:10:14. Monographs are reviewed and/or updated multiple times per month and at least once per year.
Natural Medicines disclaims any responsibility related to medical consequences of using any medical product. Effort is made to ensure that the information contained in this monograph is accurate at the time it was published. Consumers and medical professionals who consult this monograph are cautioned that any medical or product related decision is the sole responsibility of the consumer and/or the health care professional. A legal License Agreement sets limitations on downloading, storing, or printing content from this Database. No reproduction of this monograph or any content from this Database is permitted without written permission from the publisher. It is unlawful to download, store, or distribute content from this site.