Magnolia
Scientific names: Magnolia biondii, Magnolia fargesii, Magnolia denudata, Magnolia conspicua, Magnolia yulan, Magnolia heptaperta, Magnolia virginiana, Magnolia glauca, Magnolia obovata, Magnolia hypoleuca, Magnolia officinalis, Magnolia sprengeri, Magnolia sargentiana, Magnolia emargenata, Magnolia wilsonii, Magnolia nicholsoniana, Magnolia taliensis, Magnolia salicifolia, Buergeria salicifolia, Magnolia proctoriana
Family: Magnoliaceae
Alternate names: Beaver Tree, Bourgeon Floral de Magnolia, Chuan Houpu, Cortex Magnoliae Officinalis, Flos Magnoliae, Holly Bay, Ho-No-Ki, Hou Po, Hou Po Hua, Houpohua, Houpo, Houpu, Indian Bark, Japanese Whitebark Magnolia, Koboku, Magnolia, Magnolia Bark, Magnolia Flower Bud, Magnolia Rouge, Red Bay, Red Magnolia, Swamp Laurel, Swamp Sassafras, Sweet Bay, Tuhoupu, White Bay, White Laurel, Xin Ye Hua, Xin Yi Hua, Xinyi, Xinyihua
Actions: Antimicrobial, Anticancer, Antidiabetes, Anti-inflammatory, Antiplatelet, Cardiovascular, CNS, Gastrointestinal, Hormonal, Respiratory, Weight loss
Background
Magnolia (Magnolia biondii) is a plant found in parts of Asia and North and South America. The bark and flowers are used in Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Magnolia seems to have anxiety-reducing effects. Chemicals in magnolia might kill bacteria in the mouth which might help prevent cavities or reduce gum swelling.
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, magnolia is used to treat the "stagnation of qi" as well as for depression and anxiety. People also use magnolia for obesity, stress, gingivitis, plaque, and other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support most of these uses.
Magnolia seems to have anxiety-reducing effects. Chemicals in magnolia might kill bacteria in the mouth which might help prevent cavities or reduce gum swelling.
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, magnolia is used to treat the "stagnation of qi" as well as for depression and anxiety. People also use magnolia for obesity, stress, gingivitis, plaque, and other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support most of these uses.
Safety Safety definitions
When taken by mouth: Magnolia extract is possibly safe for most people when used for up to 6 weeks.
When used in toothpaste: Magnolia is possibly safe for most people when used for up to 6 months.
When applied to the skin: There isn't enough reliable information to know if magnolia is safe. Some people may develop skin rashes when magnolia is applied to the skin.
Breast-feeding: There isn't enough reliable information to know if magnolia is safe to use when breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
Surgery: There's a concern that magnolia might slow down the nervous system too much when combined with anesthesia and other medications used during and after surgery. Magnolia might also slow blood clotting and cause bleeding during and after surgery. Stop using magnolia at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
When used in toothpaste: Magnolia is possibly safe for most people when used for up to 6 months.
When applied to the skin: There isn't enough reliable information to know if magnolia is safe. Some people may develop skin rashes when magnolia is applied to the skin.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy: Taking magnolia flower bud by mouth is unsafe during pregnancy. Magnolia might cause the uterus to contract, which could cause a miscarriage. There isn't enough reliable information to know if magnolia bark is safe to use during pregnancy. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.Breast-feeding: There isn't enough reliable information to know if magnolia is safe to use when breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
Surgery: There's a concern that magnolia might slow down the nervous system too much when combined with anesthesia and other medications used during and after surgery. Magnolia might also slow blood clotting and cause bleeding during and after surgery. Stop using magnolia at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Effectiveness
NatMed Pro rates effectiveness based on scientific evidence according to the following scale: Effective, Likely Effective, Possibly Effective, Possibly Ineffective, Likely Ineffective, Ineffective, and Insufficient Evidence to Rate.
Possibly effective Effectiveness definitions
- A mild form of gum disease (gingivitis). Chewing gum or using a toothpaste containing magnolia extract seems to reduce the swelling and bleeding of gums.
Dosing & administration
Magnolia is used in toothpastes, chewing gum, and dietary supplements. There isn't enough reliable information to know what an appropriate dose of magnolia might be. Keep in mind that natural products are not always necessarily safe and dosages can be important. Be sure to follow relevant directions on product labels and consult a healthcare professional before using.
Interactions with pharmaceuticals
Medications that slow blood clotting (Anticoagulant / Antiplatelet drugs)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Magnolia might slow blood clotting. Taking magnolia along with medications that also slow blood clotting might increase the risk of bruising and bleeding.
Sedative medications (CNS depressants)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Magnolia might cause sleepiness and slowed breathing. Some medications, called sedatives, can also cause sleepiness and slowed breathing. Taking magnolia with sedative medications might cause breathing problems and/or too much sleepiness.
Interactions with herbs & supplements
Herbs and supplements that might slow blood clotting: Magnolia might slow blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might increase the risk of bleeding in some people. Examples of supplements with this effect include garlic, ginger, ginkgo, nattokinase, and Panax ginseng.
Herbs and supplements with sedative properties: Magnolia might cause sleepiness and slowed breathing. Taking it along with other supplements with similar effects might cause too much sleepiness and/or slowed breathing in some people. Examples of supplements with this effect include hops, kava, L-tryptophan, melatonin, and valerian.
Herbs and supplements with sedative properties: Magnolia might cause sleepiness and slowed breathing. Taking it along with other supplements with similar effects might cause too much sleepiness and/or slowed breathing in some people. Examples of supplements with this effect include hops, kava, L-tryptophan, melatonin, and valerian.
Interactions with foods
There are no known interactions with foods.
Products
View all productsPer 5 g:
RRP: $54.90$41.17Save: 25%
Discontinued by Henry Blooms
Create account
Practitioner product
Per tablet:
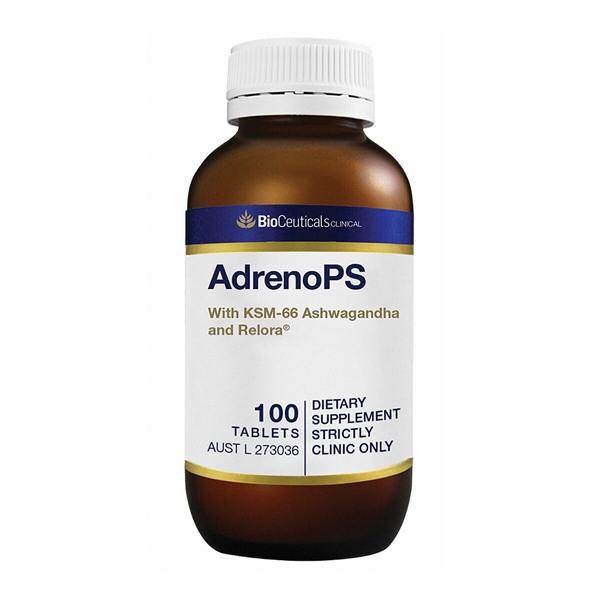
- Relora®
- Magnolia officinalis (Magnolia) ext. 51.56 mg equiv. honokiol 2.81 mg
- Withania somnifera ext. 150 mg
- Glycyrrhiza glabra ext. 250 mg
- Phosphatidylserine enriched soy (powder) (Lecithin) 50 mg equiv. phosphatidylserine 10 mg
- Calcium pantothenate (Vitamin B5) 27.29 mg equiv. pantothenic acid 25 mg equiv. calcium 2.29 mg
- Pyridoxal 5-phosphate monohydrate (P5P) 7.84 mg equiv. pyridoxine 5 mg
Practitioner product
Per tablet:
RRP: $49.95$37.47Save: 25%
Create account
Per tablet:
RRP: $26.79$24.11Save: 10%
Create account
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
RRP: $61.59$55.43Save: 10%
Create account
RRP: $61.00$48.80Save: 20%
Create account
Per tablet:
Practitioner product
Per capsule:
- Magnolia liliflora (Xin Yi Hua) ext. 37.312 mg
- Morus alba ext. 37.312 mg
- Mentha haplocalyx ext. 37.312 mg
- Chrysanthemum sinense ext. 29.85 mg
- Angelica dahurica ext. 22.387 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis ext. 22.387 mg
- Xanthium sibiricum ext. 22.387 mg
- Cinnamomum cassia (bark) ext. 22.387 mg
- Anemone altaica ext. 22.387 mg
- Schizonepeta tenuifolia ext. 22.387 mg
Practitioner product
Per capsule:
RRP: $36.60$30.37Save: 17%
OOS at supplier
Create account
return unknown
Per capsule:
- Magnolia liliflora (Xin Yi Hua) ext. 26.1 mg
- Lonicera japonica ext. 43.2 mg
- Phragmites australis ext. 34.5 mg
- Forsythia suspensa ext. 34.5 mg
- Mentha haplocalyx ext. 26.1 mg
- Prunus armeniaca ext. 26.1 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis ext. 26.1 mg
- Fritillaria thunbergii ext. 26.1 mg
- Peucedanum praeruptorum ext. 26.1 mg
- Platycodon grandiflorus ext. 17.4 mg
- Glycyrrhiza uralensis ext. 13.8 mg
Practitioner product
Per capsule:
- Magnolia liliflora (Xin Yi Hua) ext. 20.4 mg
- Atractylodes macrocephala ext. 22.5 mg
- Astragalus membranaceus ext. 27 mg
- Rehmannia glutinosa ext. 22.5 mg
- Morus alba ext. 22.5 mg
- Lycium chinense ext. 22.5 mg
- Xanthium sibiricum ext. 20.4 mg
- Angelica dahurica ext. 20.4 mg
- Mentha haplocalyx ext. 20.4 mg
- Pseudostellaria heterophylla ext. 20.4 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis ext. 20.4 mg
- Pueraria lobata ext. 20.4 mg
- Atractylodes lancea ext. 19.8 mg
- Saposhnikovia divaricata ext. 20.4 mg
Practitioner product
Per capsule:
- Magnolia liliflora (Xin Yi Hua) ext. 20.16 mg
- Lonicera japonica ext. 26.88 mg
- Forsythia suspensa ext. 26.88 mg
- Mentha haplocalyx ext. 26.88 mg
- Morus alba ext. 26.88 mg
- Chrysanthemum sinense ext. 20.16 mg
- Xanthium sibiricum ext. 20.16 mg
- Angelica dahurica ext. 20.16 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis ext. 20.13 mg
- Gardenia jasminoides ext. 20.13 mg
- Schizonepeta tenuifolia ext. 20.13 mg
- Ligusticum sinense ext. 20.13 mg
- Glycyrrhiza uralensis ext. 11.16 mg
Practitioner product
RRP: $51.95$44.17Save: 15%
Create account
vital.ly has licensed monographs from TRC Healthcare.
This monograph was last reviewed on 14/02/2025 11:00:00 and last updated on 04/06/2018 18:44:10. Monographs are reviewed and/or updated multiple times per month and at least once per year.
Natural Medicines disclaims any responsibility related to medical consequences of using any medical product. Effort is made to ensure that the information contained in this monograph is accurate at the time it was published. Consumers and medical professionals who consult this monograph are cautioned that any medical or product related decision is the sole responsibility of the consumer and/or the health care professional. A legal License Agreement sets limitations on downloading, storing, or printing content from this Database. No reproduction of this monograph or any content from this Database is permitted without written permission from the publisher. It is unlawful to download, store, or distribute content from this site.