Oregano
Scientific names: Origanum vulgare
Family: Lamiaceae/Labiatae
Alternate names: Carvacrol, Dostenkraut, European Oregano, Huile d'Origan, Marjolaine Bâtarde, Marjolaine Sauvage, Marjolaine Vivace, Mediterranean Oregano, Mountain Mint, Oil of Oregano, Oregano Oil, Organy, Origan, Origan Européen, Origani Vulgaris Herba, Origano, Origanum, Phytoprogestin, Spanish Thyme, Thé Sauvage, Thym des Bergers, Wild Marjoram, Winter Marjoram, Wintersweet
Actions: Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Antiviral
Background
Oregano (Origanum vulgare) is an herb used to flavor foods. It is considered safe in common food amounts, but has little evidence of health benefits.
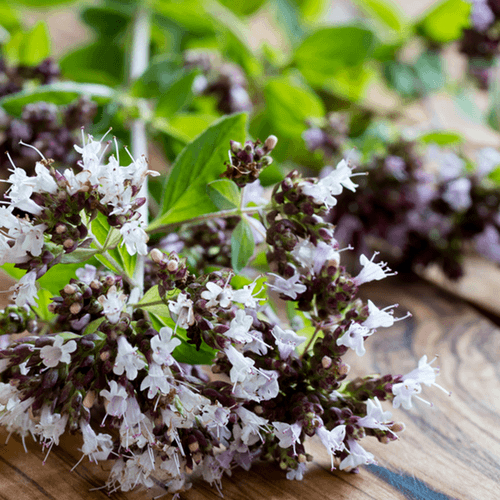
Oregano has olive-green leaves and purple flowers. It is closely related to other herbs, including mint, thyme, marjoram, and basil. Oregano contains chemicals that might help reduce cough. Oregano also might help with digestion and with fighting against some bacteria and viruses.
People use oregano for wound healing, parasite infections, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
Oregano has olive-green leaves and purple flowers. It is closely related to other herbs, including mint, thyme, marjoram, and basil. Oregano contains chemicals that might help reduce cough. Oregano also might help with digestion and with fighting against some bacteria and viruses.
People use oregano for wound healing, parasite infections, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
Safety Safety definitions
When taken by mouth: Oregano leaf and oregano oil are likely safe when eaten in foods. There isn't enough reliable information to know if oregano is safe to use in amounts greater than those found in food. Mild side effects include stomach upset.
When applied to the skin: There isn't enough reliable information to know if oregano oil is safe to apply to the skin. It may cause irritation when applied in concentrations greater than 1%.
Breast-feeding: There isn't enough reliable information to know if large amounts of oregano are safe to use when breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and stick to food amounts.
Allergies: Oregano can cause reactions in people allergic to Lamiaceae family plants, including basil, hyssop, lavender, marjoram, mint, and sage.
Surgery: Large doses of oregano might increase the risk of bleeding. People who use large doses of oregano should stop taking oregano 2 weeks before surgery.
When applied to the skin: There isn't enough reliable information to know if oregano oil is safe to apply to the skin. It may cause irritation when applied in concentrations greater than 1%.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy: Oregano is possibly unsafe when taken by mouth in medicinal amounts during pregnancy. There is concern that taking oregano in amounts larger than food amounts might cause miscarriage. Stay on the safe side and stick to food amounts.Breast-feeding: There isn't enough reliable information to know if large amounts of oregano are safe to use when breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and stick to food amounts.
Allergies: Oregano can cause reactions in people allergic to Lamiaceae family plants, including basil, hyssop, lavender, marjoram, mint, and sage.
Surgery: Large doses of oregano might increase the risk of bleeding. People who use large doses of oregano should stop taking oregano 2 weeks before surgery.
Effectiveness
Effective Effectiveness definitions
There is interest in using oregano for a number of purposes, but there isn't enough reliable information to say whether it might be helpful.
Dosing & administration
Fresh and dried oregano leaf and oregano oil are commonly eaten in foods. As a supplement, there isn't enough reliable information to know what an appropriate dose of oregano might be. Keep in mind that natural products are not always necessarily safe and dosages can be important. Be sure to follow relevant directions on product labels and consult a healthcare professional before using.
Interactions with pharmaceuticals
Medications for diabetes (Antidiabetes drugs)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Oregano might lower blood sugar levels. Taking oregano along with diabetes medications might cause blood sugar to drop too low. Monitor your blood sugar closely.
Medications that slow blood clotting (Anticoagulant / Antiplatelet drugs)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Oregano might slow blood clotting. Taking oregano along with medications that also slow blood clotting might increase the risk of bruising and bleeding.
Interactions with herbs & supplements
Copper: Oregano might decrease the absorption of copper into the body. But it isn't clear if this is a big concern.
Herbs and supplements that might lower blood sugar: Oregano might lower blood sugar. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might lower blood sugar too much. Examples of supplements with this effect include aloe, bitter melon, cassia cinnamon, chromium, and prickly pear cactus.
Herbs and supplements that might slow blood clotting: Oregano might slow blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might increase the risk of bleeding in some people. Examples of supplements with this effect include garlic, ginger, ginkgo, nattokinase, and Panax ginseng.
Iron: Oregano might decrease the absorption of iron into the body. But it isn't clear if this is a big concern.
Zinc: Oregano might decrease the absorption of zinc into the body. But it isn't clear if this is a big concern.
Herbs and supplements that might lower blood sugar: Oregano might lower blood sugar. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might lower blood sugar too much. Examples of supplements with this effect include aloe, bitter melon, cassia cinnamon, chromium, and prickly pear cactus.
Herbs and supplements that might slow blood clotting: Oregano might slow blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding. Taking it with other supplements with similar effects might increase the risk of bleeding in some people. Examples of supplements with this effect include garlic, ginger, ginkgo, nattokinase, and Panax ginseng.
Iron: Oregano might decrease the absorption of iron into the body. But it isn't clear if this is a big concern.
Zinc: Oregano might decrease the absorption of zinc into the body. But it isn't clear if this is a big concern.
Interactions with foods
There are no known interactions with foods.
Products
View all productsRRP: $30.50$24.40Save: 20%
Create account
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
RRP: $29.95$26.96Save: 10%
Create account
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Practitioner product
Per 5 g (Cucumber Lime):
- Origanum vulgare (Oregano) powder 50 mg
- Brassica oleracea var. italica powder 250 mg
- Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) 100 mg
- Cordyceps sinensis 105 mg
- Lentinula edodes 100 mg
- Trametes versicolor 70 mg
- Astragalus membranaceus 100 mg
- Camellia sinensis 500 mg
- Grifola frondosa 125 mg
- Spinacia oleracea (Spinach) 175 mg
- Brassica oleracea var. acephala (leaf) powder (Kale) 175 mg
- Nasturtium officinale 160 mg
- Apium graveolens powder 110 mg
- Pleurotus eryngii 100 mg
- Lipase 750 LipU
- Protease 1000 DU
- Ananas comosus (Bromelain) 350 GDU
- Carica papaya (Papain) 40 mg
- L-glutamine 500 mg
- Bacillus coagulans 4 billion CFU
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus 750 million CFU
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae (boulardii) (SB) 500 million CFU
- Quercetin 100 mg
- Taraxacum officinale 100 mg
- Coriandrum sativum 80 mg
- Zingiber officinale 50 mg
- Rosmarinus officinalis 50 mg
- Natural flavours
- Stevia rebaubiana ext.
- Eleutherococcus senticosus 100 mg
- Citric acid anhydrous
- Chlorella vulgaris powder 175 mg
150 g Cucumber Lime
RRP: $59.95$53.96Save: 10%
Create account
Practitioner product
RRP: $29.70$26.73Save: 10%
Create account
RRP: $46.95$37.55Save: 20%
Create account
Per 10 g (X Immuno Tonic):
- Origanum vulgare (Oregano)
- Beef bones
- Sea salt
- Curcuma longa
- Piper nigrum
- Chilli powder
- Honey
- Apple cider vinegar
- Allium sativum
- Armoracia rusticana
- Zingiber officinale
- Daucus carota powder (Carrot)
- Apium graveolens
- Allium cepa
- Malus (Apple)
- Orange
- Citrus limon (Lemon)
- Brassica juncea
- Petroselinum crispum
- Rosmarinus officinalis
- Thymus vulgaris
- Juniperus communis (berry)
- Bay leaf
- Szechuan pepper
- Backhousia citriodora
- Pink Himalayan crystal salt
390 g X Immuno Tonic
RRP: $39.00$33.15Save: 15%
Create account
Per 3 g:
- Origanum vulgare (Oregano)
- Echinacea angustifolia
- Astragalus membranaceus
- Sambucus nigra (fruit)
- Lycium barbarum
- Rosa canina
- Luo Han Guo (fruit) ext. (Monk fruit)
- Echinacea purpurea
- Sambucus nigra
- Glycyrrhiza glabra (root)
- Olea europaea (leaf)
- Calendula officinalis
- Uncaria tomentosa
- Mentha x piperita
- Thymus vulgaris
- Cola acuminata
- Foeniculum vulgare
- Inula helenium
- Asclepias tuberosa
- Achillea millefolium
- Armoracia rusticana
- Capsicum spp.
- Allium sativum
- Allium cepa
- Zingiber officinale
- Cordyceps sinensis (mushroom)
- Ganoderma lucidum (mushroom)
- Lentinula edodes (mushroom)
- Tremella fuciformis (mushroom)
- Trametes versicolor (mushroom)
- Salvia eremostachya
- Hericium erinaceus (mushroom)
- Inonotus obliquus (mushroom)
- Ilex paraguariensis
RRP: $49.95$47.45Save: 5%
Create account
Practitioner product
Per 5 g (Chocolate Malt):
- Origanum vulgare (Oregano) oil
- Hordeum vulgare (Barley)
- Green banana starch 250 mg
- Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina)
- Quercetin 200 mg
- Brassica oleracea var. italica (Broccoli)
- Apple pectin 50 mg
- Larix occidentalis (arabinogalactan) (Larch) 250 mg
- Bacillus coagulans 25 mg
- Punica granatum
- Macrocystis pyrifera (Ocean kelp)
- Brassica oleracea var. acephala (leaf & sprout) powder (Kale)
- Spinacia oleracea (Spinach)
- Daucus carota powder (Carrot)
- Brassica oleracea var. viridis
- Palmaria palmata (Dulse)
- Apium graveolens (seed) powder
- Petroselinum crispum
- Citrus bioflavonoids extract 150 mg
- Myrciaria dubia (fruit) powder (Camu Camu)
- Malpighia glabra
- Blueberry flavour
- Zingiber officinale
- Kakadu plum powder
- Theobroma cacao (Cocoa powder)
- Natural flavours
- Pink Himalayan crystal salt
- Ananas comosus (Bromelain) 150 mg
- Thymus vulgaris oil
- Syzygium aromaticum oil
- Mentha x piperita oil
- N-acetyl glucosamine (NAG) 125 mg
- Stevia rebaubiana
- Zinc citrate 7.5 mg
- Chlorella vulgaris powder
- Polyphenolic fulvic minerals 50 mg
150 g Chocolate Malt
RRP: $59.99$52.80Save: 12%
Create account
Per 10 g (Manuka Honey, Ginger & Cinnamon):
390 g Manuka Honey, Ginger & Cinnamon
RRP: $33.99$30.59Save: 10%
Create account
RRP: $18.50$15.73Save: 15%
OOS at supplier
Create account
return unknown
vital.ly has licensed monographs from TRC Healthcare.
This monograph was last reviewed on 31/07/2024 10:00:00 and last updated on 01/03/2023 09:42:24. Monographs are reviewed and/or updated multiple times per month and at least once per year.
Natural Medicines disclaims any responsibility related to medical consequences of using any medical product. Effort is made to ensure that the information contained in this monograph is accurate at the time it was published. Consumers and medical professionals who consult this monograph are cautioned that any medical or product related decision is the sole responsibility of the consumer and/or the health care professional. A legal License Agreement sets limitations on downloading, storing, or printing content from this Database. No reproduction of this monograph or any content from this Database is permitted without written permission from the publisher. It is unlawful to download, store, or distribute content from this site.