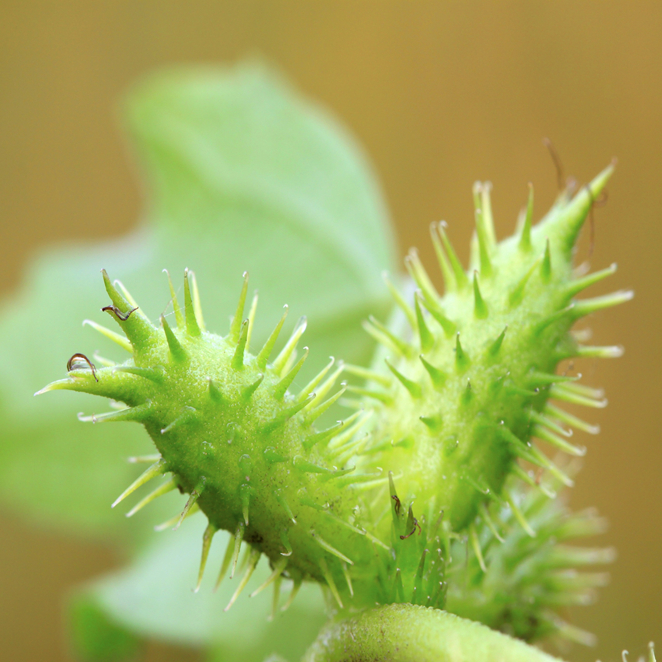
Background
People use Siberian cocklebur for conditions such as long-term swelling (inflammation) of the airways in the lungs (chronic bronchitis), common cold, constipation, diabetes, and many others, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses. Using Siberian cocklebur can also be unsafe.
Safety Safety definitions
There isn't enough reliable information to know if Siberian cocklebur fruit is safe or what the side effects might be.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: Siberian cocklebur is LIKELY UNSAFE when the seeds and seedlings are taken by mouth. Deaths have been reported. Avoid using.Children: Siberian cocklebur is LIKELY UNSAFE when the seeds and seedlings are taken by mouth. Deaths have been reported. It is POSSIBLY UNSAFE when the Siberian fruit is taken by mouth. There has been a report of a 20-month old child dying after taking Siberian cocklebur fruit by mouth for 2 months.
Diabetes: Siberian cocklebur lowers blood sugar levels. Do not use Siberian cocklebur if you have diabetes.
Liver disease: Siberian cocklebur causes liver toxicity and, in some cases, liver failure. Do not use Siberian cocklebur if you have liver disease or you are at risk of liver disease.
Kidney disease: Siberian cocklebur causes kidney toxicity. Do not use Siberian cocklebur if you have kidney disease or you are at risk of kidney disease.
Surgery: Siberian cocklebur interferes with blood sugar control. This is a problem during and after surgery. Stop taking Siberian cocklebur at least 2 weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Effectiveness
- Long-term swelling (inflammation) of the airways in the lungs (chronic bronchitis).
- Common cold.
- Constipation.
- Swelling (inflammation) of the nasal cavity and sinuses (rhinosinusitis).
- Stuffy nose.
- Itching.
- Hives (urticaria).
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
- Diabetes.
- Headache.
- Tuberculosis.
- Kidney disease.
- Other conditions.
Dosing & administration
Interactions with pharmaceuticals
Medications for diabetes (Antidiabetes drugs)
Interaction Rating=Major Do not take this combination.
Siberian cocklebur decreases blood sugar. Diabetes medications are also used to lower blood sugar. Taking Siberian cocklebur with diabetes medications can make blood sugar levels fall too low. Do not take Siberian cocklebur if you are using diabetes medications.
Some medications used for diabetes include glimepiride (Amaryl), glyburide (DiaBeta, Glynase PresTab, Micronase), insulin, metformin (Glucophage), pioglitazone (Actos), rosiglitazone (Avandia), chlorpropamide (Diabinese), glipizide (Glucotrol), tolbutamide (Orinase), and others.
Medications that can harm the kidneys (Nephrotoxic Drugs)
Interaction Rating=Major Do not take this combination.
Siberian cocklebur can harm the kidneys. Some medications can also harm the kidneys. Do not take Siberian cocklebur if you are using medications that can harm the kidneys.
Some medications that can harm the kidneys include cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune); aminoglycosides including amikacin (Amikin), gentamicin (Garamycin, Gentak, others), and tobramycin (Nebcin, others); nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) including ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, Nuprin, others), indomethacin (Indocin), naproxen (Aleve, Anaprox, Naprelan, Naprosyn), piroxicam (Feldene); and numerous others.
Medications that can harm the liver (Hepatotoxic drugs)
Interaction Rating=Major Do not take this combination.
Siberian cocklebur can harm the liver. Some medications can also harm the liver. Do not take Siberian cocklebur if you are using a medication that can harm the liver.
Some medications that can harm the liver include acetaminophen (Tylenol and others), amiodarone (Cordarone), carbamazepine (Tegretol), isoniazid (INH), methotrexate (Rheumatrex), methyldopa (Aldomet), fluconazole (Diflucan), itraconazole (Sporanox), erythromycin (Erythrocin, Ilosone, others), phenytoin (Dilantin), lovastatin (Mevacor), pravastatin (Pravachol), simvastatin (Zocor), and many others.
Interactions with herbs & supplements
Herbs and supplements that might lower blood sugar: Siberian cocklebur lowers blood sugar levels. Some herbs and supplements also lower blood sugar levels. Taking Siberian cocklebur with herbs and supplements that might lower blood sugar can make blood sugar levels fall too low. Do not take Siberian cocklebur with herbs and supplements that might lower blood sugar.
Some herbs and supplements that might lower blood sugar include alpha-lipoic acid, bitter melon, chromium, devil's claw, fenugreek, garlic, guar gum, horse chestnut, Panax ginseng, psyllium, Siberian ginseng, and others.
Interactions with foods
Action
Products
View all products- Xanthium sibiricum (Cang Er Zi) ext. 22.387 mg
- Magnolia liliflora ext. 37.312 mg
- Morus alba ext. 37.312 mg
- Mentha haplocalyx ext. 37.312 mg
- Chrysanthemum sinense ext. 29.85 mg
- Angelica dahurica ext. 22.387 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis ext. 22.387 mg
- Cinnamomum cassia (bark) ext. 22.387 mg
- Anemone altaica ext. 22.387 mg
- Schizonepeta tenuifolia ext. 22.387 mg
- Xanthium sibiricum (Cang Er Zi) ext. 20.4 mg
- Atractylodes macrocephala ext. 22.5 mg
- Astragalus membranaceus ext. 27 mg
- Rehmannia glutinosa ext. 22.5 mg
- Morus alba ext. 22.5 mg
- Lycium chinense ext. 22.5 mg
- Magnolia liliflora ext. 20.4 mg
- Angelica dahurica ext. 20.4 mg
- Mentha haplocalyx ext. 20.4 mg
- Pseudostellaria heterophylla ext. 20.4 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis ext. 20.4 mg
- Pueraria lobata ext. 20.4 mg
- Atractylodes lancea ext. 19.8 mg
- Saposhnikovia divaricata ext. 20.4 mg
- Xanthium sibiricum (Cang Er Zi) ext. 20.16 mg
- Lonicera japonica ext. 26.88 mg
- Forsythia suspensa ext. 26.88 mg
- Mentha haplocalyx ext. 26.88 mg
- Morus alba ext. 26.88 mg
- Chrysanthemum sinense ext. 20.16 mg
- Magnolia liliflora ext. 20.16 mg
- Angelica dahurica ext. 20.16 mg
- Scutellaria baicalensis ext. 20.13 mg
- Gardenia jasminoides ext. 20.13 mg
- Schizonepeta tenuifolia ext. 20.13 mg
- Ligusticum sinense ext. 20.13 mg
- Glycyrrhiza uralensis ext. 11.16 mg
- Xanthium sibiricum (Siberian cocklebur) ext. 125 mg
- Angelica dahurica ext. 142.9 mg
- Houttuynia cordata ext. 150 mg
- Magnolia liliiflora ext. 112.5 mg
- Mentha haplocalyx ext. 65 mg