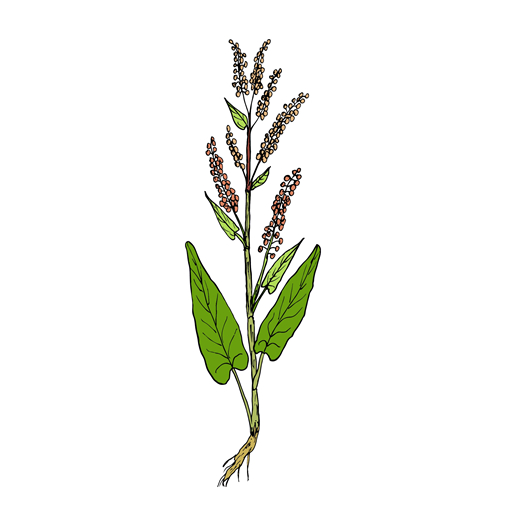
Yellow dock
Scientific names: Rumex crispus, Rumex obtusifolius
Family: Polygonaceae
Alternate names: Acedera, Amalvelas, Broad-Leaved Dock, Chukkah, Curled Dock, Curly Dock, Field Sorrel, Herbe à Cochons, Lengua de Vaca, Narrow Dock, Oseille Crépue, Parelle Sauvage, Patience Crépue, Romaza, Rumex, Sheep Sorrel, Sour Dock, Yellowdock
Actions: Antimalarial, Antioxidant, Astringent, Bile, Laxative
Background
Yellow dock (Rumex crispus) is a common weed found in Serbia, Korea, and China. The leaf stalks are used in salads. The root and fruits are used as medicine.
Yellow dock contains chemicals that work as laxatives and have anti-inflammatory effects. It also contains chemicals that might kill parasites, bacteria, and fungi.
People use yellow dock for pain, swelling of the nasal passages and the respiratory tract, constipation, hemorrhoids, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
Don't confuse yellow dock with sorrel or wood sorrel. These are not the same.
Yellow dock contains chemicals that work as laxatives and have anti-inflammatory effects. It also contains chemicals that might kill parasites, bacteria, and fungi.
People use yellow dock for pain, swelling of the nasal passages and the respiratory tract, constipation, hemorrhoids, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
Don't confuse yellow dock with sorrel or wood sorrel. These are not the same.
Safety Safety definitions
When taken by mouth: Yellow dock is possibly safe when prepared properly and consumed in amounts found in food. There isn't enough reliable information to know if properly prepared yellow dock is safe when used in amounts greater than those found in foods. But raw or uncooked yellow dock is possibly unsafe. It can cause serious side effects including vomiting, heart problems, breathing difficulty, and even death.
Blood clotting problems: Yellow dock may speed up or slow down clotting. If you have a clotting disorder or take a blood thinning medicine, talk to a healthcare provider before taking yellow dock.
Allergies: People who are allergic to ragweed may also be allergic to yellow dock.
Gastrointestinal (GI) conditions: Don't use yellow dock if you have a GI condition. Yellow dock can irritate the lining of the stomach and intestine, making some GI conditions worse.
Kidney stones: Yellow dock contains a chemical that can bind with calcium and form crystals that can damage the kidneys. If you have kidney stones or have ever had kidney stones, talk to your healthcare provider before taking yellow dock.
Special Precautions & Warnings:
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: Taking yellow dock by mouth is possibly unsafe while pregnant or breast-feeding. It has laxative effects, which are not wanted during pregnancy. Also, the chemicals that cause the laxative effects can be transferred to a nursing infant through breast milk.Blood clotting problems: Yellow dock may speed up or slow down clotting. If you have a clotting disorder or take a blood thinning medicine, talk to a healthcare provider before taking yellow dock.
Allergies: People who are allergic to ragweed may also be allergic to yellow dock.
Gastrointestinal (GI) conditions: Don't use yellow dock if you have a GI condition. Yellow dock can irritate the lining of the stomach and intestine, making some GI conditions worse.
Kidney stones: Yellow dock contains a chemical that can bind with calcium and form crystals that can damage the kidneys. If you have kidney stones or have ever had kidney stones, talk to your healthcare provider before taking yellow dock.
Effectiveness
Effective Effectiveness definitions
There is interest in using yellow dock for a number of other purposes, but there isn't enough reliable information to say whether it might be helpful.
Dosing & administration
Yellow dock has traditionally been used by adults in teas, alcohol extracts, and tinctures. But there isn't enough reliable information to know what an appropriate dose of yellow dock might be. Keep in mind that natural products are not always necessarily safe and dosages can be important. Be sure to follow relevant directions on product labels and consult a healthcare professional before using.
Interactions with pharmaceuticals
Digoxin (Lanoxin)
Interaction Rating=Major Do not take this combination.
Yellow dock is a type of laxative called a stimulant laxative. Stimulant laxatives can decrease potassium levels in the body. Low potassium levels can increase the risk of side effects from digoxin.
Warfarin (Coumadin)
Interaction Rating=Moderate Be cautious with this combination.
Yellow dock can work as a laxative and cause diarrhea. Diarrhea can increase the effects of warfarin and increase the risk of bleeding.
Water pills (Diuretic drugs)
Interaction Rating=Major Do not take this combination.
Yellow dock is a laxative. Some laxatives can cause diarrhea and decrease potassium levels. "Water pills" can also decrease potassium levels. Taking yellow dock along with "water pills" might make potassium levels drop too low.
Interactions with herbs & supplements
Calcium: Yellow dock contains a chemical that binds with calcium. This prevents calcium from being absorbed from the digestive tract. This might decrease the amount of calcium the body absorbs from supplements.
Herbs that contain cardiac glycosides: Yellow dock contains chemicals that can affect the heart. These chemicals are called cardiac glycosides. Using it along with other supplements that also contain cardiac glycosides can increase the risk of heart damage. Examples of supplements that contain cardiac glycosides include black hellebore, foxglove, lily-of-the-valley, oleander, and pleurisy root.
Iron: Yellow dock contains a chemical that binds with iron. This prevents iron from being absorbed from the digestive tract. This might decrease the amount of iron the body absorbs from supplements.
Stimulant laxative herbs: Yellow dock is a type of laxative called a stimulant laxative. Stimulant laxatives can cause diarrhea and decrease potassium levels. Taking yellow dock with other supplements with similar effects might cause more diarrhea and very low potassium levels. Examples of supplements with this effect include aloe, alder buckthorn, gossypol, rhubarb, and senna.
Zinc: Yellow dock contains a chemical that binds with zinc. This prevents zinc from being absorbed from the digestive tract. This might decrease the amount of zinc the body absorbs from supplements.
Herbs that contain cardiac glycosides: Yellow dock contains chemicals that can affect the heart. These chemicals are called cardiac glycosides. Using it along with other supplements that also contain cardiac glycosides can increase the risk of heart damage. Examples of supplements that contain cardiac glycosides include black hellebore, foxglove, lily-of-the-valley, oleander, and pleurisy root.
Iron: Yellow dock contains a chemical that binds with iron. This prevents iron from being absorbed from the digestive tract. This might decrease the amount of iron the body absorbs from supplements.
Stimulant laxative herbs: Yellow dock is a type of laxative called a stimulant laxative. Stimulant laxatives can cause diarrhea and decrease potassium levels. Taking yellow dock with other supplements with similar effects might cause more diarrhea and very low potassium levels. Examples of supplements with this effect include aloe, alder buckthorn, gossypol, rhubarb, and senna.
Zinc: Yellow dock contains a chemical that binds with zinc. This prevents zinc from being absorbed from the digestive tract. This might decrease the amount of zinc the body absorbs from supplements.
Interactions with foods
Avoid taking yellow dock with food. It contains chemicals that bind with certain minerals, including calcium, iron, and zinc, which keeps them from being absorbed by the body.
Products
View all productsPractitioner product
Practitioner product
Per tablet:
RRP: $49.95$39.96Save: 20%
Create account
Per 1 mL:
- Rumex crispus
- Bryonia alba
- Kalium bichromicum
- Sanguinaria canadensis
- Spongia tosta
- Aconitum napellus (Aconite)
- Atropa belladonna
- Hyoscyamus niger
- Phosphorus
RRP: $23.99$19.20Save: 20%
Create account
Per 0.52 mL:
- Rumex crispus
- Antimony potassium tartrate trihydrate (Ant tart)
- Atropa belladonna
- Bryonia alba
- Drosera
- Aconitum napellus (Aconite)
- Ipecacuanha
- Anemone pulsatilla (Pasque flower)
- Sticta pulmonaria
Practitioner product
Per 1 mL:
RRP: $20.99$16.79Save: 20%
OOS at supplier
Create account
return unknown
vital.ly has licensed monographs from TRC Healthcare.
This monograph was last reviewed on 17/06/2024 10:00:00 and last updated on 01/05/2022 07:39:01. Monographs are reviewed and/or updated multiple times per month and at least once per year.
Natural Medicines disclaims any responsibility related to medical consequences of using any medical product. Effort is made to ensure that the information contained in this monograph is accurate at the time it was published. Consumers and medical professionals who consult this monograph are cautioned that any medical or product related decision is the sole responsibility of the consumer and/or the health care professional. A legal License Agreement sets limitations on downloading, storing, or printing content from this Database. No reproduction of this monograph or any content from this Database is permitted without written permission from the publisher. It is unlawful to download, store, or distribute content from this site.